Sustainability in Business: US Companies’ Green Path

Navigating the intricate landscape of sustainability in business: opportunities and challenges for US companies is crucial, as firms grapple with evolving consumer demands, regulatory pressures, and the undeniable imperative of environmental stewardship, all while seeking competitive advantages and long-term resilience.
The concept of Sustainability in Business: Opportunities and Challenges for US Companies is no longer just a niche concern; it’s a fundamental pillar of modern corporate strategy. Businesses across the United States are increasingly recognizing that integrating sustainable practices isn’t merely an ethical imperative, but a significant driver of innovation, efficiency, and long-term value creation.
The Evolving Landscape of Corporate Sustainability
Corporate sustainability has transformed from a peripheral add-on to a strategic core for many US companies. This shift is driven by a confluence of factors, including heightened consumer expectations, stringent regulatory frameworks, and a growing awareness of the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic factors.
Understanding this evolving landscape is critical for any business aiming to thrive in the 21st century. It involves more than just environmental compliance; it encompasses a holistic approach to operations that considers people, planet, and profit.
Redefining Business Value Through ESG
The rise of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria has provided a standardized framework for evaluating corporate sustainability performance. Investors, consumers, and regulators are increasingly using ESG metrics to assess a company’s overall health and future viability. This shift means that businesses must move beyond anecdotal claims and demonstrate measurable progress in their sustainability endeavors.
-
Environmental Stewardship: Beyond Compliance
- Minimizing carbon footprint through renewable energy adoption.
- Implementing efficient waste management and circular economy principles.
- Protecting biodiversity and natural resources within supply chains.
For US companies, this often translates into investing in energy-efficient technologies, adopting sustainable sourcing practices, and developing products designed for longevity and recyclability. The drive towards net-zero emissions, while ambitious, is becoming a guiding principle for many industry leaders.
Stakeholder Pressure and Brand Reputation
Consumers, particularly younger generations, are demonstrating a strong preference for brands that align with their values for sustainability. This consumer activism, combined with scrutiny from NGOs and media, means that a company’s sustainability performance directly impacts its brand reputation and market perception.
Employees also play a significant role, with many seeking employment at companies that demonstrate a genuine commitment to social and environmental responsibility. A strong sustainability ethos can enhance employee engagement, retention, and attract top talent in a competitive labor market.
In essence, the evolving landscape demands transparency, accountability, and genuine commitment. Simply “greenwashing” is no longer an option; authentic, verifiable sustainable practices are becoming prerequisites for long-term success.
Opportunities for US Companies in Sustainable Practices
Embracing sustainability presents a wealth of opportunities for US businesses beyond mere compliance. These advantages span from enhanced financial performance to improved market positioning and reduced operational risks. Companies that proactively integrate sustainable practices often find themselves at the forefront of innovation and competitive advantage.
Innovation and New Market Creation
The push for sustainability naturally fosters innovation. Companies are prompted to rethink conventional processes, develop new materials, and design more efficient products and services. This drives the creation of entirely new markets and revenue streams, particularly in areas like clean energy, sustainable packaging, and eco-friendly manufacturing.
For instance, significant investments in renewable energy technologies not only reduce operational costs but also position companies as leaders in a rapidly expanding sector. Similarly, developing products with a lower environmental footprint can open doors to new consumer segments and partnerships.
Operational Efficiencies and Cost Savings
Many sustainable initiatives directly lead to significant cost reductions. Implementing energy-efficient systems, optimizing water usage, and reducing waste generation can considerably lower operational expenses. Investing in renewable energy sources, for example, can hedge against volatile fossil fuel prices.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Upgrading to LED lighting, efficient HVAC systems, and smart building technology.
- Waste Minimization: Implementing recycling programs, optimizing packaging, and exploring industrial symbiosis.
- Water Conservation: Adopting closed-loop systems and efficient irrigation in operations.
Beyond direct operational savings, reduced consumption of raw materials and better waste management can also lead to lower procurement costs and disposal fees, contributing directly to the bottom line.
Enhanced Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty
A strong commitment to sustainability can significantly boost a company’s brand image. Consumers are increasingly discerning, choosing brands that align with their environmental and social values. Companies perceived as environmentally responsible often enjoy higher customer loyalty and are more resilient to negative publicity.
This positive perception also extends to corporate storytelling, allowing businesses to communicate their values and impact, building stronger emotional connections with their target audience. This is particularly true for US markets, where consumer awareness of climate change and social justice issues is high.
Ultimately, the opportunities provided by sustainability initiatives are diverse and impactful. They represent a fundamental shift in how businesses can create value, ensuring both profitability and planetary well-being. Proactive engagement in these areas allows US companies not only to mitigate risks but to truly differentiate themselves in a competitive global economy.
Challenges Facing US Companies in Sustainability Adoption
While the business case for sustainability is compelling, US companies encounter several significant hurdles in fully integrating and scaling sustainable practices. These challenges range from financial constraints and regulatory complexities to supply chain intricacies and the inherent resistance to change within large organizations.
Initial Investment Costs and ROI Perception
One of the primary barriers is the perceived high upfront cost of transitioning to sustainable operations. Investing in new, energy-efficient machinery, renewable energy infrastructure, or sustainable materials can require substantial capital outlays. Many companies, especially smaller ones, may struggle with these initial expenditures, even if the long-term return on investment (ROI) is favorable.
Furthermore, demonstrating a clear and immediate ROI for some sustainability initiatives can be challenging. Benefits like enhanced brand reputation or reduced regulatory risk are often intangible in the short term, making it difficult to justify investments against immediate financial pressures.
Regulatory Complexity and Policy Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape concerning sustainability in the US can be fragmented and unpredictable, varying significantly between federal, state, and local levels. This patchwork of regulations creates complexity for businesses operating across different jurisdictions, making compliance a daunting task.
- Varying Emissions Standards: Differences in state-level GHG emission reduction targets.
- Waste Disposal Regulations: Diverse rules for industrial waste management across counties.
- Reporting Requirements: Inconsistent corporate sustainability reporting mandates.
Policy uncertainty, particularly concerning federal environmental policies, can also deter long-term investments in sustainable infrastructure. Companies need clear, stable policy signals to make confident, strategic decisions regarding sustainability.
Supply Chain Integration and Transparency
Achieving true sustainability requires deep integration throughout the entire supply chain, not just within a company’s direct operations. This presents a formidable challenge, as it involves engaging with numerous suppliers, often globally, to ensure their practices align with sustainability goals.
Lack of transparency in complex supply chains makes it difficult to track the environmental and social impact of every component and process. Ensuring labor standards, ethical sourcing, and environmental compliance across diverse geographical locations can be resource-intensive and require robust monitoring systems.
Overcoming these challenges necessitates a multi-faceted approach, combining strategic planning, financial innovation, advocacy for consistent policy, and collaborative efforts across entire value chains. Addressing these hurdles is crucial for US companies to successfully navigate their sustainability journey.
Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Impact
The regulatory environment plays a pivotal role in shaping the sustainability agenda for US companies. Federal, state, and even local policies can either incentivize or impede progress, creating a complex web of requirements and opportunities that businesses must navigate.
Understanding these frameworks is essential for compliance and for leveraging policy support to accelerate sustainable transformations. The impact of policy extends beyond mere legal obligations, influencing market dynamics and investment flows toward greener solutions.
Federal Initiatives and Directives
At the federal level, various agencies contribute to sustainability policy. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets standards for air and water quality, waste management, and chemical use. More broadly, policies related to clean energy tax credits, infrastructure spending, and sustainable procurement practices at federal agencies signal governmental priorities.
Recent administrations have also emphasized climate change mitigation and adaptation, which has led to initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions across sectors. These often involve specific targets or reporting requirements that compel companies to re-evaluate their operational footprints.
State and Local Policy Divergence
One of the most significant complexities for US companies is the wide divergence in state and local sustainability policies. States like California and New York often lead with more aggressive climate targets and renewable energy mandates, creating a mosaic of regulations. This can pose challenges for businesses operating nationally, requiring bespoke compliance strategies for different regions.
Local ordinances, such as bans on single-use plastics or specific building energy codes, further complicate the picture. While these policies aim to address localized environmental concerns, they add layers of complexity to corporate sustainability programs that seek to achieve uniformity across operations.
- California’s AB 32: Pioneering greenhouse gas emission reduction targets for industries.
- New York’s Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (CLCPA): Ambitious renewable energy and emission reduction goals.
- Local Plastic Bans: Numerous cities implementing restrictions on single-use items.
The interplay of these regulations can create both compliance burdens and unique market advantages. Companies that successfully navigate this diverse landscape can gain a competitive edge by adapting quickly to new standards and even influencing policy development through advocacy.
Ultimately, a dynamic regulatory landscape demands constant vigilance and strategic alignment from US companies. Proactive engagement with policy developments and effective internal governance are crucial for both mitigating risks and seizing the opportunities that emergent frameworks present.
Stakeholder Engagement and Reporting Standards
Effective sustainability initiatives are rarely developed in isolation. They require robust engagement with a diverse array of stakeholders, from employees and customers to investors, regulators, and local communities. Transparent and consistent reporting of sustainability performance is equally critical, building trust and demonstrating accountability.
Engaging Key Stakeholders
Stakeholder engagement is about fostering dialogue and integrating diverse perspectives into a company’s sustainability strategy. This process can unveil hidden risks, identify new opportunities, and ensure that sustainability efforts are meaningful and impactful across all affected groups.
-
Employees: Internal Champions of Change
- Involving employees in waste reduction programs or energy-saving initiatives fosters a culture of sustainability.
- Providing training on sustainable practices can empower staff to identify efficiencies and innovate.
Beyond internal stakeholders, engaging customers through feedback mechanisms, investors through transparent disclosures, and local communities through partnerships and outreach programs ensures broader alignment and support for sustainability goals. This collaborative approach often leads to more robust and widely accepted outcomes.
The Importance of Transparent Reporting
In an era of increasing scrutiny, comprehensive and transparent sustainability reporting is no longer optional. It serves as a vital tool for communicating a company’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to external audiences. This includes detailing progress on commitments, outlining challenges, and providing data-backed insights.
Various reporting frameworks have emerged to standardize this disclosure, offering companies guidelines on what and how to report. Companies adopting such standards benefit from enhanced credibility and comparability with peers.
- GRI (Global Reporting Initiative): Comprehensive framework for various sustainability aspects.
- SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board): Industry-specific standards focused on financially material ESG issues.
- TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures): Focuses on climate-related financial risk and opportunity disclosures.
Adhering to these standards helps investors make informed decisions, allows consumers to evaluate companies based on their values, and facilitates regulatory oversight. Moreover, the process of preparing these reports often helps companies identify areas for improvement within their own operations.
Ultimately, a strong commitment to both proactive stakeholder engagement and rigorous, transparent reporting forms the bedrock of a credible and impactful corporate sustainability strategy. These practices are fundamental to building long-term trust and fostering sustained progress in the US business environment.
Future Trends and Emerging Imperatives
The trajectory of sustainability in business indicates a future where environmental and social considerations are even more deeply embedded in corporate DNA. For US companies, staying abreast of these emerging trends and imperatives is crucial for competitiveness and resilience in the decades to come. This involves preparing for shifts in technology, consumer behavior, and global interconnectedness.
Accelerated Adoption of Decarbonization Technologies
The push towards net-zero emissions will accelerate the adoption of advanced decarbonization technologies. This includes not only renewable energy like solar and wind but also advancements in carbon capture, energy storage, and green hydrogen. Companies that invest in and integrate these technologies will gain significant competitive advantages, both in terms of operational efficiency and market reputation.
Furthermore, digital technologies like AI and blockchain will play a greater role in optimizing resource use, improving supply chain transparency, and enabling more effective impact measurement. Smart grids and predictive analytics will help sectors manage energy demand and supply more efficiently.
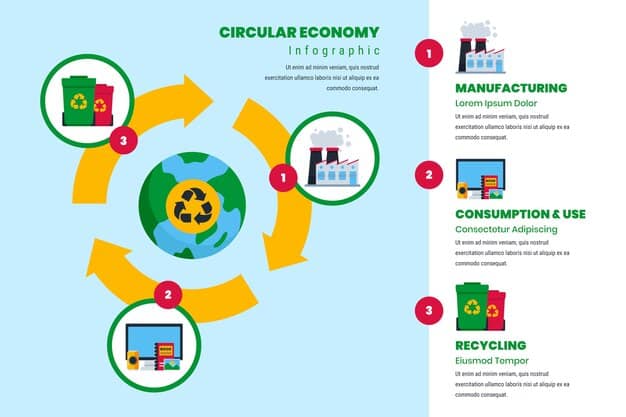
Circular Economy as a Business Model
The linear “take-make-dispose” model is increasingly being replaced by circular economy principles. This paradigm shift focuses on designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. For US companies, this means rethinking product design, supply chains, and end-of-life management.
- Product-as-a-Service Models: Shifting from selling products to providing access and retaining ownership for repair and recycling.
- Recycled Content Mandates: Growing demand for products made from post-consumer recycled materials.
- Industrial Symbiosis: Collaborations where waste from one company becomes a resource for another.
Embracing the circular economy offers opportunities for new business models, reduced reliance on virgin resources, and enhanced material security, leading to long-term economic and environmental benefits.

Increased Focus on Social Equity and Just Transition
While environmental concerns have often dominated sustainability discussions, the “social” aspect of ESG is gaining increasing prominence. Future trends will see a stronger emphasis on social equity, ensuring that the transition to a sustainable economy is fair and inclusive, particularly for vulnerable communities. This includes addressing issues of diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), fair labor practices, and community engagement.
Companies will be expected to demonstrate how their sustainability strategies contribute to a “just transition,” ensuring that workers and communities are not left behind as industries transform. This proactive approach to social impact will be crucial for maintaining a strong social license to operate and building long-term stakeholder trust.
These emerging trends highlight that sustainability is not a static goal but a dynamic journey. US companies that anticipate and adapt to these evolving imperatives will be better positioned to thrive, demonstrating leadership and creating enduring value in a rapidly changing world.
Building a Resilient and Responsible Business for Tomorrow
In a world marked by rapid environmental shifts and heightened societal expectations, building a resilient and responsible business is paramount for US companies. This involves not only mitigating risks but also proactively embedding sustainability as a core component of strategic planning and day-to-day operations. The journey towards true sustainability is continuous, demanding adaptability and a long-term vision.
Integrating Sustainability into Core Business Strategy
Sustainability should not be an isolated department or an afterthought; it must be woven into the very fabric of a company’s mission, vision, and operational strategies. This means that environmental and social considerations are integrated into decision-making processes across all functions, from product development and supply chain management to finance and marketing.
Companies that adopt this integrated approach tend to see sustainability not as a cost center but as a value driver, unlocking new efficiencies, fostering innovation, and strengthening stakeholder relationships. It enables a more holistic view of risk management and opportunity identification.
The Role of Leadership and Corporate Culture
Transformative change towards sustainability begins at the top. Strong leadership commitment is essential to drive sustainability initiatives throughout an organization. Leaders must champion the cause, allocate necessary resources, and foster a culture where sustainability is a shared responsibility, not just a mandate.
A corporate culture that values environmental stewardship, social equity, and ethical governance empowers employees at all levels to contribute to sustainable outcomes. This internal alignment is critical for overcoming resistance to change and for ensuring that sustainability efforts are consistently implemented and continually improved upon.
Measuring Impact and Demonstrating Progress
What gets measured gets managed. Effectively measuring the environmental and social impact of business operations is crucial for demonstrating progress, identifying areas for improvement, and building credibility with stakeholders. This involves setting clear, quantifiable targets and regularly reporting against them using credible methodologies.
Beyond traditional financial metrics, companies are increasingly tracking their carbon footprint, water usage, waste diversion rates, diversity metrics, and community investment. This data-driven approach allows for transparent communication of successes and challenges, reinforcing accountability and fostering continuous improvement.
In conclusion, the path to a resilient and responsible business future for US companies is paved with strategic integration, committed leadership, and transparent measurement. By embracing these principles, businesses can not only navigate the complexities of sustainability but emerge stronger, more innovative, and truly prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌱 Market Opportunities | Sustainability drives innovation, opens new markets, and enhances brand reputation, offering competitive advantages. |
| 💼 Operational Efficiency | Investing in sustainable practices often leads to significant cost savings through reduced energy, water, and waste. |
| 🚧 Core Challenges | High initial investment, regulatory complexity, and supply chain transparency remain significant hurdles for businesses. |
| 📈 Future Trends | Decarbonization, circular economy models, and social equity are critical future imperatives for US companies. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Business Sustainability
Sustainability is crucial for US businesses due to heightened consumer demand for eco-friendly products, stricter environmental regulations, and growing investor focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors. Embracing sustainability helps improve brand reputation, reduces operational costs through efficiency, and mitigates risks associated with climate change and resource scarcity.
Opportunities include significant cost savings from reduced energy and waste, enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty, improved access to capital from ESG-focused investors, and the potential for innovation leading to new products or market segments. Sustainability can also attract and retain top talent who prioritize working for responsible companies.
Key challenges include high upfront investment costs for green technologies, difficulties in measuring and demonstrating immediate ROI, complex and inconsistent regulatory frameworks across states, and ensuring transparency and sustainability throughout intricate global supply chains. Overcoming internal resistance to change can also be a significant hurdle.
Regulatory frameworks, spanning federal to local levels, set compliance standards for environmental protection (e.g., emissions, waste). They can also incentivize sustainable practices through tax credits or grants. However, the varied and sometimes uncertain nature of these policies across different jurisdictions can create complications for national businesses.
Future trends include accelerated adoption of decarbonization technologies, a stronger shift towards circular economy business models focusing on reuse and recycling, and an increased emphasis on social equity and a just transition for all stakeholders. Digital tools, like AI and blockchain, will also play a larger role in driving efficiency and transparency in sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for a Sustainable Business Future
The journey toward full sustainability for US companies is undeniably complex, marked by both transformative opportunities and formidable challenges. From the imperative of decarbonization to the intricate demands of supply chain transparency, businesses are navigating a landscape continuously reshaped by consumer expectations, regulatory evolution, and the undeniable reality of climate change. Yet, embracing these shifts is not merely about compliance; it’s about reshaping business models for resilience, fostering innovation, and securing long-term prosperity. Companies that prioritize integrating environmental, social, and governance principles into their core strategies, supported by robust leadership and transparent reporting, will not only contribute meaningfully to a healthier planet but also unlock significant competitive advantages, strengthening their market position and building trust among all stakeholders. The future of business is intrinsically linked to its commitment to a sustainable tomorrow.